Formation of geosynclines
The classic geosyncline is divided into two parts, namely a miogeocline, and a eugeocline which lies to the seaward side. The miogeocline is made up of sediments which form the continental shelf. The eugeocline consists of sediments on the continental rise in deeper water some distance offshore. If subsidence continues in spurts, more than one eugeocline can form, with the associated miogeocline lying on top of the previous eugeocline. A current example is the sedimentary section of the continental rise that lies seaward off the continental slope off the eastern United States.
Landward
of the rise and capping the continental shelf is a wedge of sediments
that becomes progressively thicker as it extends towards the shelf
edge. This wedge is the miogeocline and is really a very young
geosyncline, before it is fully formed. The sediments are soft
and relatively un-compacted.
The source of sediments for the geosynclinal prism is from the continental craton. In the North American example, the majority of sediments from the continent are eventually dumped into the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Mexico.
Geosynclinal prisms are deposited along the trailing edge of a plate. If the continental plate changes its relative direction of motion, and the trailing edge becomes a leading edge, the geosyncline is compressed and folded. This has happened in eastern North America and caused the folding of the Appalachian Mountains. Sedimentation to form a geosyncline and subsequent folding constitutes a basic geologic cycle which evolves over several hundred million years, and may be repeated several times. Currently, the opening of the North Atlantic is progressing at the rate of 3 cm per year.
The great sedimentary basin stretching from the Canadian Arctic through western Canada and the western United States to the Gulf of Mexico is another example of a geosyncline. The continental edge (miogeocline) was to the east and the seaward edge (eugeocline) was to the west. This geosyncline is being uplifted and folded by the pressure created by the collision of the North American plate with the Pacific Ocean plate.



 Rifting
Rifting  سن نسبی
سن نسبی  What is Petrified Wood
What is Petrified Wood  دوره های زمین شناسی
دوره های زمین شناسی  کتاب زمین شناسی تاریخی استاد محمدرضا کبریایی
کتاب زمین شناسی تاریخی استاد محمدرضا کبریایی  unconformity
unconformity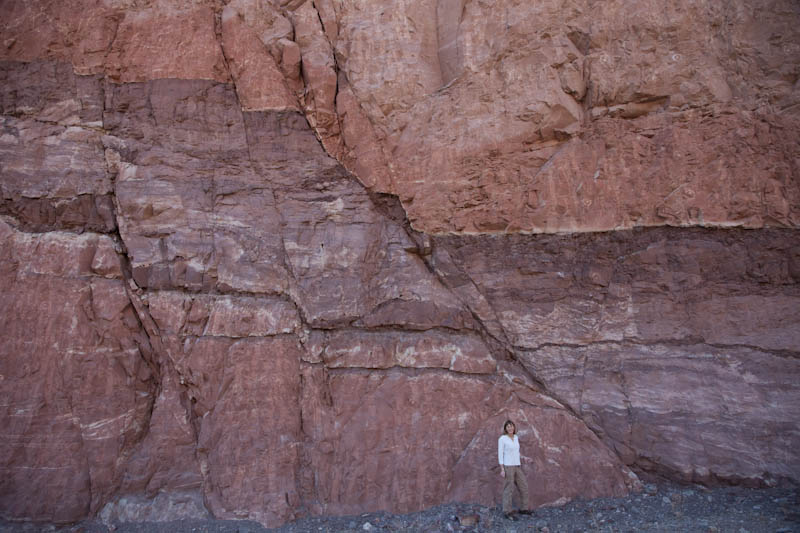 Fault
Fault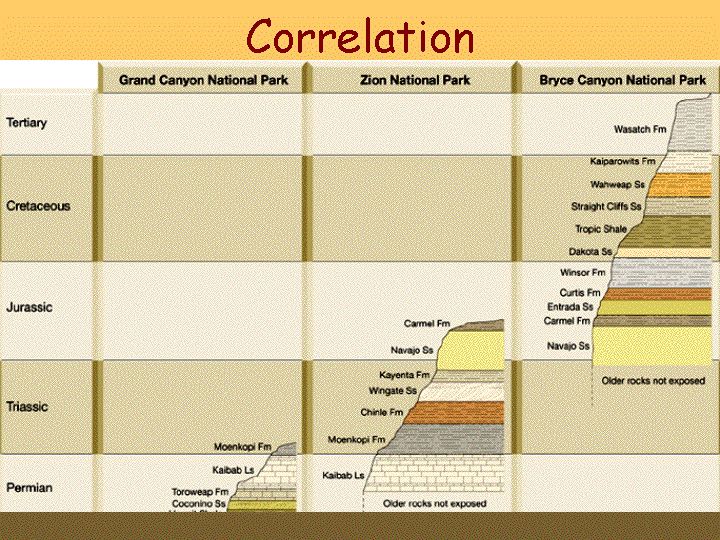 Correlation
Correlation BIF
BIF ساختار زمین
ساختار زمین کهکشان آندرومدا
کهکشان آندرومدا کهکشان مارپیچی
کهکشان مارپیچی مراحل دگر ریختی
مراحل دگر ریختی  Monitoring Bárðarbunga and Holuhraun
Monitoring Bárðarbunga and Holuhraun اطلس استرس های افقی جهان
اطلس استرس های افقی جهان